High-throughput protease activity cytometry reveals dose-dependent heterogeneity in PMA-mediated ADAM17 activation†
Abstract
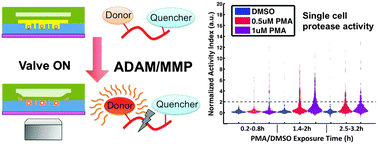
As key components of autocrine signaling, pericellular proteases, a disintegrin and metalloproteinases (ADAMs) in particular, are known to impact the microenvironment of individual cells and have significant implications in various pathological situations including cancer, inflammatory and vascular diseases. There is great incentive to develop a high-throughput platform for single-cell measurement of pericellular protease activity, as it is essential for studying the heterogeneity of protease response and the corresponding cell behavioral consequences. In this work, we developed a microfluidic platform to simultaneously monitor protease activity of many single cells in a time-dependent manner. This platform isolates individual microwells rapidly on demand and thus allows single-cell activity measurement of both cell-surface and secreted proteases by confining individual cells with diffusive FRET-based substrates. With this platform, we observed dose-dependent heterogeneous protease activation of HepG2 cells treated with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA). To study the temporal behavior of PMA-induced protease response, we monitored the pericellular protease activity of the same single cells during three different time periods and revealed the diversity in the dynamic patterns of single-cell protease activity profile upon PMA stimulation. The unique temporal information of single-cell protease response can help unveil the complicated functional role of pericellular proteases.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...