Morus nigra leaf extract improves glycemic response and redox profile in the liver of diabetic rats
Abstract
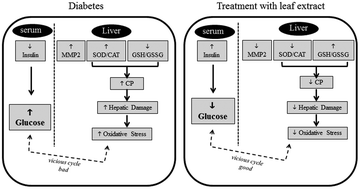
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by hyperglycemia and alterations in the carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism. DM is associated with increased oxidative stress and pancreatic beta cell damage, which impair the production of insulin and the maintenance of normoglycemia. Inhibiting oxidative damage and controlling hyperglycemia are two important strategies for the prevention of diabetes. The pulp and leaf extracts of mulberry (Morus nigra L.) have abundant total phenolics and flavonoids, and its antioxidant potential may be an important factor for modulating oxidative stress induced by diabetes. In this study, DM was induced by intraperitoneal injection of alloxan monohydrate (135 mg kg−1). Female Fischer rats were divided into four groups: control, diabetic, diabetic pulp, and diabetic leaf extract. Animals in the diabetic pulp and diabetic leaf extract groups were treated for 30 days with M. nigra L. pulp or leaf extracts, respectively. At the end of treatment, animals were euthanized and, liver and blood samples were collected for analysis of biochemical and metabolic parameters. Our study demonstrated that treatment of diabetic rats with leaf extracts decreased the superoxide dismutase (SOD)/catalase (CAT) ratio and carbonylated protein levels by reducing oxidative stress. Moreover, the leaf extract of M. nigra L. decreased the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 activity, increased insulinemia, and alleviated hyperglycemia-induced diabetes. In conclusion, our study found that the leaf extract of M. nigra L. improved oxidative stress and complications in diabetic rats, suggesting the utility of this herbal remedy in the prevention and treatment of DM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...