Pathways for solar photovoltaics†
Abstract
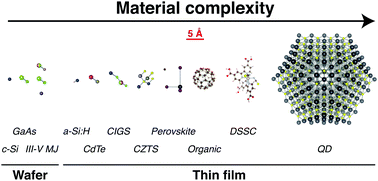
Solar energy is one of the few renewable, low-carbon resources with both the scalability and the technological maturity to meet ever-growing global demand for electricity. Among solar power technologies, solar photovoltaics (PV) are the most widely deployed, providing 0.87% of the world's electricity in 2013 and sustaining a compound annual growth rate in cumulative installed capacity of 43% since 2000. Given the massive scale of deployment needed, this article examines potential limits to PV deployment at the terawatt scale, emphasizing constraints on the use of commodity and PV-critical materials. We propose material complexity as a guiding framework for classifying PV technologies, and we analyze three core themes that focus future research and development: efficiency, materials use, and manufacturing complexity and cost.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...