Intramolecular C–H oxidative addition to iridium(i) triggered by trimethyl phosphite in N,N′-diphosphanesilanediamine complexes†‡
Abstract
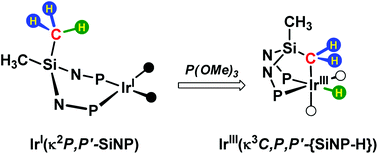
The reaction of [Ir(SiNP)(cod)][PF6] ([1][PF6]) and of IrCl(SiNP)(cod) (5) (SiNP = SiMe2{N(4-C6H4CH3)PPh2}2) with trimethyl phosphite affords the iridium(III) derivatives of the formula [IrHClx(SiNP-H){P(OMe)3}2−x](1−x)+ (x = 0, 3+; x = 1, 6) containing the κ3C,P,P′-coordinated SiNP-H ligand (SiNP-H = Si(CH2)(CH3){N(4-C6H4CH3)PPh2}2). The thermally unstable pentacoordinated cation [Ir(SiNP){P(OMe)3}(cod)]+ (2+) has been detected as an intermediate of the reaction and has been fully characterised in solution. Also, the mechanism of the C–H oxidative addition has been elucidated by DFT calculations showing that the square planar iridium(I) complexes of the formula [IrClx(SiNP){P(OMe)3}2−x](1−x)+ (x = 0, 4+; x = 1, 7) should be firstly obtained from 2+ and finally should undergo the C–H oxidative addition to iridium(I) via a concerted intramolecular mechanism. The influence of the counterion of 2+ on the outcome of the C–H oxidative addition reaction has also been investigated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...