Actinide (An = Th–Pu) dimetallocenes: promising candidates for metal–metal multiple bonds†
Abstract
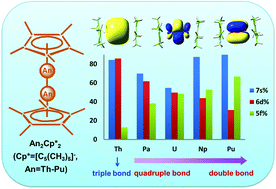
Synthesis of complexes with direct actinide–actinide (An–An) bonding is an experimental ‘holy grail’ in actinide chemistry. In this work, a series of actinide dimetallocenes An2Cp*2 (Cp* = C5(CH3)5, An = Th–Pu) with An–An multiple bonds have been systematically investigated using quantum chemical calculations. The coaxial Cp*–An–An–Cp* structures are found to be the most stable species for all the dimetallocenes. A Th–Th triple bond is predicted in the Th2Cp*2 complex, and the calculated An–An bond orders decrease across the actinide series from Pa to Pu. The covalent character of the An–An bonds is analyzed by using natural bond orbitals (NBO), molecular orbitals (MO), the quantum theory of atoms in molecules (QTAIM), and electron density difference (EDD). While Th 6d orbitals dominate the Th–Th bonds in Th2Cp*2, the An 6d-orbital characters decrease and 5f-orbital characters increase for complexes from Pa2Cp*2 to Pu2Cp*2. All these actinide dimetallocenes are stable in the gas phase relative to the AnCp* reference at room temperature. Based on the reactions of AnCp*2 and An, Th2Cp*2, Pa2Cp*2 and possibly also U2Cp*2 should be accessible as isolated molecules under suitable synthetic conditions. Our results shed light on the molecular design of ligands for stabilizing actinide–actinide multiple bonds.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...