Tricarbonyl 99mTc(i) and Re(i)–thiosemicarbazone complexes: synthesis, characterization and biological evaluation for targeting bacterial infection†
Abstract
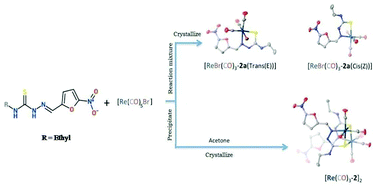
Methyl, ethyl and phenyl nitrofuryl thiosemicarbazone ligands (1, 2 and 3 respectively) were radiolabeled with freshly prepared aqueous solution of a fac[99mTc(CO)3(H2O)3]+ precursor. The radiochemical yield was around 98% as determined by thin layer chromatography and HPLC. The complexes exhibited substantial stability. The corresponding Re(I) complexes were prepared from a Re(CO)5Br precursor to understand the coordination behavior of the ligands against a tricarbonyl rhenium(I) precursor. The rhenium(I) complexes were characterized by means of IR, NMR and mass spectroscopic studies as well as by X-ray crystallography, and correlated with the technetium complexes by means of HPLC studies. Electrochemical reduction of monomeric Re(CO)3-complexes of nitrofuryl ethyl thiosemicarbazone was also studied using cyclic voltammetry. Biodistribution studies of 99mTc(CO)3-labeled thiosemicarbazones in rats intramuscularly infected with S. aureus exhibited substantial in vivo stability of the complex and moderate accumulation at the site of focal infection.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...