Reduction of mixed Mn–Zr oxides: in situ XPS and XRD studies
Abstract
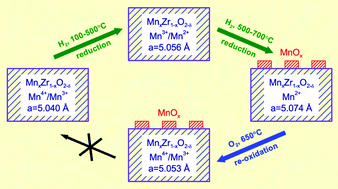
A series of mixed Mn–Zr oxides with different molar ratios Mn/Zr (0.1–9) have been prepared by coprecipitation of manganese and zirconium nitrates and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and BET methods. It has been found that at concentrations of Mn below 30 at%, the samples are single-phase solid solutions (MnxZr1−xO2−δ) based on a ZrO2 structure. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) measurements showed that manganese in these solutions exists mainly in the Mn4+ state on the surface. An increase in Mn content mostly leads to an increase in the number of Mn cations in the structure of solid solutions; however, a part of the manganese cations form Mn2O3 and Mn3O4 in the crystalline and amorphous states. The reduction of these oxides with hydrogen was studied by a temperature-programmed reduction technique, in situ XRD, and near ambient pressure XPS in the temperature range from 100 to 650 °C. It was shown that the reduction of the solid solutions MnxZr1−xO2−δ proceeds via two stages. During the first stage, at temperatures between 100 and 500 °C, the Mn cations incorporated into the solid solutions MnxZr1−xO2−δ undergo partial reduction. During the second stage, at temperatures between 500 and 700 °C, Mn cations segregate on the surface of the solid solution. In the samples with more than 30 at% Mn, the reduction of manganese oxides was observed: Mn2O3 → Mn3O4 → MnO.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...