A two-photon fluorescent probe for detecting endogenous hypochlorite in living cells†
Abstract
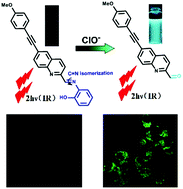
A novel two-photon fluorescent probe (HQ) for hypochlorite (ClO−) has been developed based on specific ClO−-promoted oxidation of a C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) N bond. The probe shows linear fluorescence responses to ClO− with 23.5-fold enhancement. Two-photon fluorescence detection signals of HQ to ClO− were observed with high selectivity and sensitivity. The good biocompatibility guaranteed the use of HQ to detect intracellular ClO− under two-photon excitation. Moreover, HQ has been successfully applied to monitor the endogenously produced hypochlorite in living cells (BV-2) stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). HQ provides a new ClO− detection agent for the discovery of pharmacological microglia modulators by high-throughput screening.
N bond. The probe shows linear fluorescence responses to ClO− with 23.5-fold enhancement. Two-photon fluorescence detection signals of HQ to ClO− were observed with high selectivity and sensitivity. The good biocompatibility guaranteed the use of HQ to detect intracellular ClO− under two-photon excitation. Moreover, HQ has been successfully applied to monitor the endogenously produced hypochlorite in living cells (BV-2) stimulated by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). HQ provides a new ClO− detection agent for the discovery of pharmacological microglia modulators by high-throughput screening.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...