Ca–Ca interaction in inverse sandwich Ca–C8H8–Ca†
Abstract
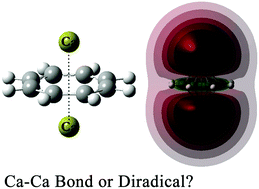
The inverse sandwich Ca–C8H8–Ca is predicted to be an open-shell singlet state. Since the C8H8 ligand prevents the spin-up and spin-down electrons of different calcium atoms from forming Ca–Ca bonds, the spin-coupling electrons lead to a singlet diradical character. The metal–ligand interaction contributes to the stability of Ca–C8H8–Ca against dissociation and isomerization. For the coordination complex (DME)3Ca–C8H8–Ca(DME)3, the open-shell singlet state is unavailable, while the closed-shell singlet state with direct Ca–Ca bonds is more favorable, because dimethyl ether molecules could push the spin-paired electrons of different calcium atoms to migrate towards the direction of Ca–Ca bonding. For Ca–C4H4–Ca, the ground state is an open-shell singlet state, of which the diradical character is very similar to that of Ca–C8H8–Ca. For (DME)3Ca–C4H4–Ca(DME)3, the lowest energy is the triplet state.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...