Dendrimer-encapsulated Pd(0) nanoparticles immobilized on nanosilica as a highly active and recyclable catalyst for the copper- and phosphine-free Sonogashira–Hagihara coupling reactions in water†
Abstract
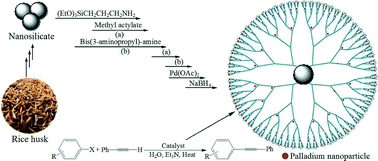
This study demonstrates a new synthetic strategy for the preparation of porous SiO2 for catalytic applications using natural and waste materials from rice husks as the source of biosilica. Biogenic porous silica nanoparticles with a mean diameter of 45 nm were successfully prepared from rice husk (RH) biomass via a new multistep method. During the first step, sodium silicate is extracted from rice husks. Then, cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB), HCl, and HOAc were added into sodium silicate solution, and the resulting mixture was sonicated. After the hydrothermal reaction, the collected samples were calcinated to obtain silica nanoparticles. Then, dendrimer-encapsulated Pd(0) nanoparticles supported on nano-silica with surface amino groups were fabricated. These materials are prepared by sequestering palladium ions within dendrimers followed by chemical reduction to yield the corresponding zero-valent palladium nanoparticles. The synthesized nanostructures were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), dynamic light scattering (DLS), N2 adsorption–desorption isotherm analysis, UV–vis spectroscopy and elemental analysis. The morphologies of the catalyst were characterized using a field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) and a transmission electron microscope (TEM). Also, its Pd content was determined by using an inductively coupled plasma (ICP) analyzer. This catalytic system was used as an efficient catalyst for Sonogashira reaction of aryl halides with alkynes under copper and phosphine ligand-free conditions in water. The catalyst was regenerated for five cycles of reaction without any significant loss in its activity. Also, the analysis of the reaction mixture by the ICP technique showed that the leaching of the catalyst was negligible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...