Excitons in poly(para phenylene vinylene): a quantum-chemical perspective based on high-level ab initio calculations†
Abstract
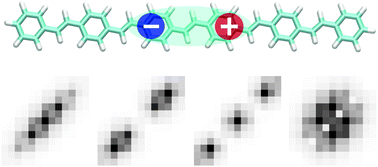
Excitonic effects play a fundamental role in the photophysics of organic semiconductors such as poly(para phenylene vinylene) (PPV). The emergence of these effects is examined for PPV oligomers based on high level ab initio excited-state calculations. The computed many-body wavefunctions are subjected to our recently developed exciton analysis protocols to provide a qualitative and quantitative characterization of excitonic effects. The discussion is started by providing high-level benchmark calculations using the algebraic-diagrammatic construction for the polarization propagator in third order of perturbation theory (ADC(3)). These calculations support the general adequacy of the computationally more efficient ADC(2) method in the case of singly excited states but also reveal the existence of low-energy doubly excited states. In a next step, a series of oligomers with chains of two to eight phenyl rings is studied at the ADC(2) level showing that the confinement effects are dominant for small oligomers, while delocalized exciton bands emerge for larger systems. In the case of the largest oligomer, the first twenty singlet and triplet excited states are computed and a detailed analysis in terms of the Wannier and Frenkel models is presented. The presence of different Wannier bands becomes apparent, showing a general trend that exciton sizes are lowered with increasing quasi-momentum within the bands.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...