Mixtures of the 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium acetate ionic liquid with different inorganic salts: insights into their interactions†
Abstract
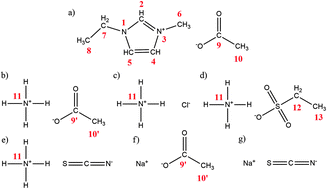
In this work, we explore the interactions between the ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolim acetate and different inorganic salts belonging to two different cation families, those based on ammonium and others based on sodium. NMR and Raman spectroscopy are used to screen for changes in the molecular environment of the ions in the ionic liquid + inorganic salt mixtures as compared to pure ionic liquid. The ion self-diffusion coefficients are determined from NMR data, allowing the discussion of the ionicity values of the ionic liquid + inorganic salt mixtures calculated using different methods. Our data reveal that preferential interactions are established between the ionic liquid and ammonium-based salts, as opposed to sodium-based salts. Computational calculations show the formation of aggregates between the ionic liquid and the inorganic salt, which is consistent with the spectroscopic data, and indicate that the acetate anion of the ionic liquid establishes preferential interactions with the ammonium cation of the inorganic salts, leaving the imidazolium cation less engaged in the media.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...