Microsolvation of methylmercury: structures, energies, bonding and NMR constants (199Hg, 13C and 17O)†
Abstract
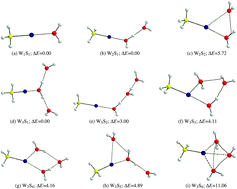
Hartree–Fock (HF) and second order perturbation theory (MP2) calculations within the scalar and full relativistic frames were carried out in order to determine the equilibrium geometries and interaction energies between cationic methylmercury (CH3Hg+) and up to three water molecules. A total of nine structures were obtained. Bonding properties were analyzed using the Quantum Theory of Atoms In Molecules (QTAIM). The analyses of the topology of electron densities reveal that all structures exhibit a partially covalent Hg⋯O interaction between methylmercury and one water molecule. Consideration of additional water molecules suggests that they solvate the (CH3Hg⋯OH2)+ unit. Nuclear magnetic shielding constants σ(199Hg), σ(13C) and σ(17O), as well as indirect spin–spin coupling constants J(199Hg–13C), J(199Hg–17O) and J(13C–17O), were calculated for each one of the geometries. Thermodynamic stability and the values of NMR constants correlate with the ability of the system to directly coordinate oxygen atoms of water molecules to the mercury atom in methylmercury and with the formation of hydrogen bonds among solvating water molecules. Relativistic effects account for 11% on σ(13C) and 14% on σ(17O), which is due to the presence of Hg (heavy atom on light atom, HALA effect), while the relativistic effects on σ(199Hg) are close to 50% (heavy atom on heavy atom itself, HAHA effect). J-coupling constants are highly influenced by relativity when mercury is involved as in J(199Hg–13C) and J(199Hg–17O). On the other hand, our results show that the values of NMR constants for carbon and oxygen, atoms which are connected through mercury (C–Hg⋯O), are highly correlated and are greatly influenced by the presence of water molecules. Water molecules introduce additional electronic effects to the relativistic effects due to the mercury atom.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...