Photoinduced charge accumulation by metal ion-coupled electron transfer†
Abstract
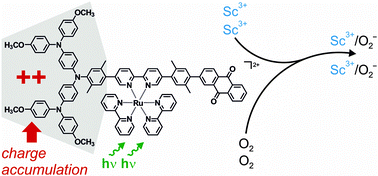
An oligotriarylamine (OTA) unit, a Ru(bpy)32+ photosensitizer moiety (Ru), and an anthraquinone (AQ) entity were combined to a molecular dyad (Ru-OTA) and a molecular triad (AQ-Ru-OTA). Pulsed laser excitation at 532 nm led to the formation of charge-separated states of the type Ru−-OTA+ and AQ−-Ru-OTA+ with lifetimes of ≤10 ns and 2.4 μs, respectively, in de-aerated CH3CN at 25 °C. Upon addition of Sc(OTf)3, very long-lived photoproducts were observed. Under steady-state irradiation conditions using a flux of (6.74 ± 0.21) × 1015 photons per second at 450 nm, the formation of twofold oxidized oligotriarylamine (OTA2+) was detected in aerated CH3CN containing 0.02 M Sc3+, as demonstrated unambiguously by comparison with UV-Vis absorption spectra obtained in the course of chemical oxidation with Cu2+. Photodriven charge accumulation on the OTA unit of Ru-OTA and AQ-Ru-OTA is possible due to the lowering of the O2 reduction potential caused by the interaction of superoxide with the strong Lewis acid Sc3+. The presence of the anthraquinone unit in AQ-Ru-OTA accelerates the rate-determining reaction step for charge accumulation by a factor of 10 compared to the Ru-OTA dyad. This is attributed to the formation of Sc3+-stabilized anthraquinone radical anion intermediates in the triad. Possible mechanistic pathways leading to charge accumulation are discussed. Photodriven charge accumulation is of key importance for solar fuels because their production will have to rely on multi-electron chemistry rather than single-electron reaction steps. Our study is the first to demonstrate that metal ion-coupled electron transfer (MCET) can be exploited to accumulate charges on a given molecular unit using visible light as an energy input. The approach of using a combination of intra- and intermolecular electron transfer reactions which are enabled by MCET is conceptually novel, and the fundamental insights gained from our study are relevant in the greater context of solar energy conversion.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...