Efficient approach to include molecular polarizations using charge and atom dipole response kernels to calculate free energy gradients in the QM/MM scheme†
Abstract
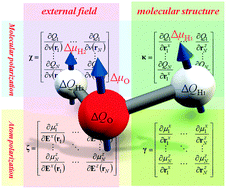
An efficient approach to evaluate free energy gradients (FEGs) within the quantum mechanical/molecular mechanical (QM/MM) framework has been proposed to clarify reaction processes on the free energy surface (FES) in molecular assemblies. The method is based on response kernel approximations denoted as the charge and the atom dipole response kernel (CDRK) model that include explicitly induced atom dipoles. The CDRK model was able to reproduce polarization effects for both electrostatic interactions between QM and MM regions and internal energies in the QM region obtained by conventional QM/MM methods. In contrast to charge response kernel (CRK) models, CDRK models could be applied to various kinds of molecules, even linear or planer molecules, without using imaginary interaction sites. Use of the CDRK model enabled us to obtain FEGs on QM atoms in significantly reduced computational time. It was also clearly demonstrated that the time development of QM forces of the solvated propylene carbonate radical cation (PC˙+) provided reliable results for 1 ns molecular dynamics (MD) simulation, which were quantitatively in good agreement with expensive QM/MM results. Using FEG and nudged elastic band (NEB) methods, we found two optimized reaction paths on the FES for decomposition reactions to generate CO2 molecules from PC˙+, whose reaction is known as one of the degradation mechanisms in the lithium-ion battery. Two of these reactions proceed through an identical intermediate structure whose molecular dipole moment is larger than that of the reactant to be stabilized in the solvent, which has a high relative dielectric constant. Thus, in order to prevent decomposition reactions, PC˙+ should be modified to have a smaller dipole moment along two reaction paths.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...