Ti/ZnO–MxOy composites (M = Al, Cr, Fe, Ce): synthesis, characterization and application as highly efficient photocatalysts for hexachlorobenzene degradation†
Abstract
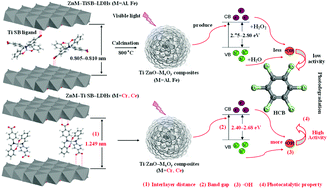
A series of novel organic–inorganic nanoscale layered materials were synthesized by intercalating the Ti-containing Schiff base complex into the interlayer of the ZnM layered double hydroxides (LDHs, M = Al, Cr, Fe, Ce). The hybrid material was further calcined to make metal oxide composites with highly dispersed Ti elements (Ti/ZnO–MxOy). The structural characterization and photocatalytic results showed that, after intercalation and calcination, the metal oxide composites with a unique flower-like crystal morphology not only had high specific surface area, uniform pore size distribution and narrow band gap, but also showed extremely high photocatalytic performance for hexachlorobenzene (HCB) degradation. The Ti/ZnO–Cr2O3 composite with the narrowest band gap (2.40 eV) and the highest surface area (227 m2) showed the highest photocatalytic performance for HCB (95.5% within 240 min) among the four metal oxide composites. Particularly, it was found that composites derived from layered materials with different supramolecular structure of the host and guest showed different photocatalytic properties. In addition, based on the results from ESR, GC-MS and HPLC-MS, the type and amount of hydroxyl radicals, the decomposition intermediates and the pathway of HCB degradation photocatalyzed by Ti/ZnO–MxOy composites are also discussed in detail.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...