Heat conduction in double-walled carbon nanotubes with intertube additional carbon atoms†
Abstract
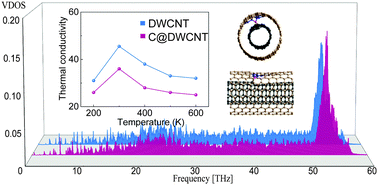
Heat conduction of double-walled carbon nanotubes (DWCNTs) with intertube additional carbon atoms was investigated for the first time using a molecular dynamics method. By analyzing the phonon vibrational density of states (VDOS), we revealed that the intertube additional atoms weak the heat conduction along the tube axis. Moreover, the phonon participation ratio (PR) demonstrates that the heat transfer in DWCNTs is dominated by low frequency modes. The added atoms cause the mode weight factor (MWF) of the outer tube to decrease and that of the inner tube to increase, which implies a lower thermal conductivity. The effects of temperature, tube length, and the number and distribution of added atoms were studied. Furthermore, an orthogonal array testing strategy was designed to identify the most important structural factor. It is indicated that the tendencies of thermal conductivity of DWCNTs with added atoms change with temperature and length are similar to bare ones. In addition, thermal conductivity decreases with the increasing number of added atoms, more evidently for atom addition concentrated at some cross-sections rather than uniform addition along the tube length. Simultaneously, the number of added atoms at each cross-section has a considerably more remarkable impact, compared to the tube length and the density of chosen cross-sections to add atoms.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...