The binding and insertion of imidazolium-based ionic surfactants into lipid bilayers: the effects of the surfactant size and salt concentration
Abstract
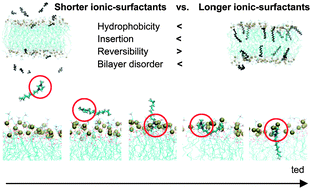
Imidazolium-based ionic surfactants with hydrocarbon tails of different sizes were simulated with lipid bilayers at different salt concentrations. Starting with the random position of ionic surfactants outside the bilayer, surfactants with long tails mostly insert into the bilayer, while those with short tails show the insertion of fewer surfactant molecules, indicating the effect of the tail length. In particular, surfactants with a tail of two or four hydrocarbons insert and reversibly detach from the bilayer, while the inserted longer surfactants cannot be reversibly detached because of the strong hydrophobic interaction with lipid tails, in quantitative agreement with experiments. Longer surfactants insert more deeply and irreversibly into the bilayer and thus increase lateral diffusivities of the bilayer, indicating that longer surfactants more significantly disorder lipid bilayers, which also agrees with experiments regarding the effect of the tail length of ionic surfactants on membrane permeability and toxicity. Addition of NaCl ions weakens the electrostatic interactions between headgroups of surfactants and lipids, leading to the binding of fewer surfactants into the bilayer. In particular, our simulation findings indicate that insertion of ionic surfactants can be initiated by either the hydrophobic interaction between tails of surfactants and lipids or the electrostatic binding between imidazolium heads and lipid heads, and the strength of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions depends on the tail length of surfactants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...