Electrochemical energy storage by polyaniline nanofibers: high gravity assisted oxidative polymerization vs. rapid mixing chemical oxidative polymerization
Abstract
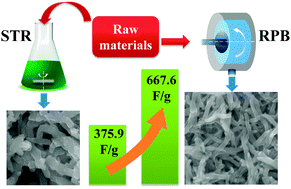
Polyaniline (PANI) nanofibers prepared by high gravity chemical oxidative polymerization in a rotating packed bed (RPB) have demonstrated a much higher specific capacitance of 667.6 F g−1 than 375.9 F g−1 of the nanofibers produced by a stirred tank reactor (STR) at a gravimetric current of 10 A g−1. Meanwhile, the cycling stability of the electrode is 62.2 and 65.9% for the nanofibers from RPB and STR after 500 cycles, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...