Low temperature phase transition induced biaxial negative thermal expansion of 2,4-dinitroanisole†
Abstract
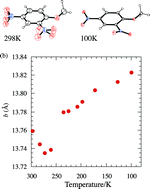
The crystal structure of 2,4-dinitroanisole (24DNAN) is known to have two polymorphic structures (Z′ = 2 and Z′ = 1, hereafter referred to as α-form and β-form, respectively) and the oxygen atoms of the nitro group(s) of both polymorphs have been found to be disordered over two positions at 298 K. In the thermal behaviour studies of 24DNAN, the β-form showed a phase transition at 264.5 K on cooling. To investigate this phase transition variable-temperature single-crystal X-ray diffraction measurements were carried out. The β angle for the β-form dramatically changed from 90.190° (298 K) to 96.716° (100 K). The length of the b axis shows negative thermal expansion, 13.741(5) to 13.810(5) Å (with a change in temperature from 298 K to 100 K). The thermal expansion coefficients along the principal axes X1, X2, and X3 are −31(6), −15(7) and 262(20) MK−1 (261–100 K), respectively. 24DNAN showed an unusual biaxial NTE induced by a low temperature phase transition.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Single-Crystal-to-Single-Crystal Transformations

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...