Semiconductor-enhanced Raman scattering for highly robust SERS sensing: the case of phosphate analysis†
Abstract
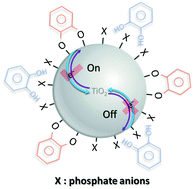
Quantitative analysis of phosphate anions was achieved by measurement of “turn-off” SERS based on the first-layer effect of a chemical mechanism. More importantly, our results demonstrate that it is possible, by means of semiconductor-enhanced Raman scattering, to enhance the SERS sensing performance including stability and reproducibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...