Cellular effects of magnetic nanoparticles explored by atomic force microscopy
Abstract
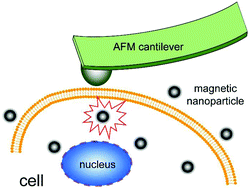
The investigation of subtle change of cells exposed to nanomaterials is extremely essential but also challenging for nanomaterial-based biological applications. In this study, atomic force microscopy (AFM) was employed to investigate the effects of iron–iron oxide core–shell magnetic nanoparticles on the mechanical properties of bovine articular chondrocytes (BACs). After being exposed to the nanoparticles even at a high nanoparticle-concentration (50 μg mL−1), no obvious difference was observed by using conventional methods, including the WST-1 assay and live/dead staining. However a significant difference of Young's modulus of the cells was detected by AFM even when the concentration of nanoparticles applied in the cell culture medium was low (10 μg mL−1). The difference of cellular Young's modulus increased with the increase of nanoparticle concentration. AFM was demonstrated to be a useful tool to identify the subtle change of cells when they were exposed to nanomaterials even at a low concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...