Heparin molecularly imprinted surfaces for the attenuation of complement activation in blood
Abstract
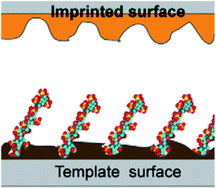
Heparin-imprinted synthetic polymer surfaces with the ability to attenuate activation of both the complement and the coagulation system in whole blood were successfully produced. Imprinting was achieved using a template coated with heparin, a highly sulfated glycosaminoglycan known for its anticoagulant properties. The N,N′-diacryloylpiperazine—methacrylic acid copolymers were characterized using goniometry, AFM and XPS. The influence of the molecular imprinting process on morphology and template rebinding was demonstrated by radioligand binding assays. Surface hemocompatibility was evaluated using human whole blood without anticoagulants followed by measurement of complement activation markers C3a and sC5b-9 and platelet consumption as a surrogate coagulation activation marker. The observed low thrombogenicity of this copolymer combined with the attenuation of complement activation induced by the molecular imprint offer potential for the development of self-regulating surfaces with important potential clinical applications. We propose a mechanism for the observed phenomena based upon the recruitment of endogenous sulfated glycosaminoglycans with heparin-like activities.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...