Surface modulation of complex stiffness via layer-by-layer assembly as a facile strategy for selective cell adhesion†
Abstract
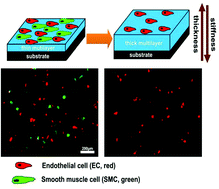
In-stent restenosis and thrombosis are the main severe problems that occur after the percutaneous vascular intervention. The competition between endothelial cells (ECs) and smooth muscle cells (SMCs) plays a key role during these pathological changes. The regulation of this competition offers new opportunities to design biomaterials in the cardiovascular fields. Bioactive molecules have been typically employed to increase EC adhesion and thereafter to enhance EC competitiveness; however, this method is associated with limitations from the point of view of practical and industrial applications. Herein, we present an approach to enhance EC competitiveness over that of SMC through the selective EC adhesion, which is achieved by modulating a complex surface stiffness based on the technique of layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly. This complex stiffness can be achieved by regulating the thickness of multilayer films coordinating with a rigid underlying substrate. The selective cell adhesion is attributed to changes in the complex surface stiffness and a different intrinsic property between ECs and SMCs. This study provides a facile and broadly applicable approach for the purpose of the enhancement of EC competitiveness over that of SMC, which has great potential for the development of cell-based functional biomaterials in the cardiovascular field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...