One-step determination of lead over a higher linear range by an artificial neural network after air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction coupled to flame atomic absorption spectrometry
Abstract
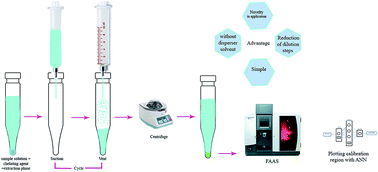
A simple and rapid method was proposed for the preconcentration of trace levels of lead prior to its determination by flame atomic absorption spectroscopy, based on air-assisted liquid–liquid microextraction. The preconcentration of the lead was mediated by chelation with 4-(2-pyridylazo) resorcinol (PAR). Several variables affecting the method such as the pH of the sample, concentration of PAR, volume of extraction solvent and number of extraction cycles were investigated, and optimized conditions were achieved. Under the optimum conditions, the calibration graph was linear in the range of 5–60 ng mL−1 lead. The limit of detection (LOD) and relative standard deviation (RSD%) for five replicate determinations (40 ng mL−1) were 1.36 ng mL−1 and 5.2%, respectively. An artificial neural network (ANN) strategy was used to extend the dynamic range (LDR) of the calibration, which prompted the LDR to increase more than three-fold (3–210 ng mL−1 approximately). The root mean square of the percentage deviations (RMSPD) was 6.55%. This strategy was successfully applied to determine the lead concentration in water samples.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...