Optimization of enzyme immobilization on magnetic microparticles using 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC) as a crosslinking agent
Abstract
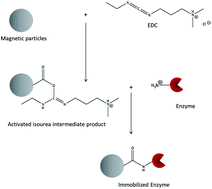
Enzyme immobilization is a versatile tool in biotransformation processes to enhance enzyme activity and to secure an easy separation of catalysts and products and the reusability of enzymes. A simple and commonly used method for crosslinking enzymes to a solid support is the zero-length crosslinking agent 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC). This work shows the optimization of the EDC-crosslinking protocol for two enzymes, glucose oxidase (GOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP), to functionalized magnetic microparticles. For GOx the optimization of the immobilization parameters pH-value and the enzyme to particle ratio results in activity yields of up to 36%, which is in the usual range for undirected enzyme immobilisations. In contrast, for HRP the activity yield does not exceed 6% even after optimization of the protocols. The main reasons for this unusually low activity yield are the presence of multiple HRP isoforms in the enzyme solution used for immobilisation and the observed tendency of HRP to be inactive even in the case of simple physisorption to the particle surface.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...