Capillary column coated with graphene quantum dots for gas chromatographic separation of alkanes and aromatic isomers†
Abstract
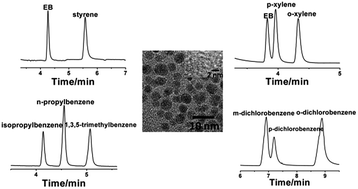
Graphene Quantum Dots (GQDs) have potential to be an excellent stationary phase because of their high surface area, adsorption affinities and rich functional groups. The rich functional groups of GQDs can form hydrogen bonding and π–π electrostatic stacking interactions with volatile aromatic compounds or unsaturated organic compounds. Herein, GQDs were explored as the stationary phase for gas chromatographic capillary column separation of alkanes and aromatic isomers with 3-aminopropyldiethoxymethyl silane (3-AMDS) as the coupling reagent. GQD coated capillary columns exhibit high separation efficiency for ethylbenzene, styrene, xylene, propylbenzene, alkanes, and dichlorobenzene isomers at low temperature. The elution sequence of the analytes follows an increasing order of their boiling points, even for p-dichlorobenzene and m-dichlorobenzene, which have close boiling points (p-dichlorobenzene, 173.4 °C, m-dichlorobenzene, 173 °C). The separation behavior of the column for different organic substances is related to van der Waals forces or π–π interactions between the test analytes and GQDs. Compared with the commercial HP-5 and HP-innowax capillary columns, GQD coated columns allowed fast and efficient separation of the analytes at low temperature without temperature-programming. The relative standard deviations (RSD) of five replicate separations for the test analytes on the GQD coated capillary column were 0.1–1.6%, 0.7–4.0%, 0.8–8.5%, and 1.2–2.2% for retention time, peak area, peak height, and half peak width, respectively.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...