Facile synthesis and screen printing of dual-mode luminescent NaYF4:Er,Yb (Tm)/carbon dots for anti-counterfeiting applications†
Abstract
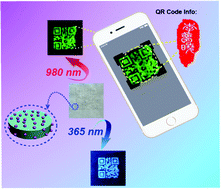
Rare-earth ion (RE3+) doped up-conversion (UC) fluorescent materials and novel fluorescent carbon quantum dots (CDs) have been widely used as traditional anti-counterfeiting materials owing to their excellent optical properties. The drawbacks of these materials are being exposed gradually with the widespread occurrence of counterfeit products in the market because of their single fluorescence mode and easy replication. In this work, we propose a novel strategy to combine both luminescent materials with different modes via a facile solvothermal method. Interesting, the composite materials show unalterable down-conversion (DC) blue light under a 365 nm ultraviolet (UV) analyzer, except for adjustable UC luminescence properties. The UC and DC optical properties are measured and the probable mechanism is proposed, indicating that the dual-mode fluorescence processes are separate and do not interference with each other. Moreover, we use a mixture containing a small number of UCMPs/CDs and poly(acrylic acid) (PAA) aqueous solution as a colorless anti-counterfeiting ink, and successfully print a variety of dual-mode fluorescence patterns through the screen printing technique, including QR codes, the logo of Wuhan University, and clover patterns. The composite materials show good dispersion and outstanding dual-mode fluorescence properties, suggesting that they are promising luminescent materials in the anti-counterfeiting field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...