Topotactic fluorination of strontium iron oxide thin films using polyvinylidene fluoride
Abstract
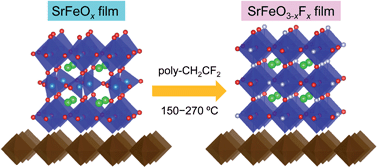
We report herein the topotactic fluorination of SrFeO3−δ thin films (δ ∼ 0, 0.5, 1) with polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF). SrFeO3−xFx epitaxial thin films were obtained by fluorination at 150–270 °C, which is substantially lower than the reaction temperature for polycrystalline bulk samples prepared with PVDF. The fluorine content (x) of the film was widely varied by controlling the PVDF-treatment temperature and/or the amount of oxygen vacancies in the precursor film. The higher reactivity of the SrFeO2 and SrFeO2.5 thin films can be reasonably explained by a fluorine-diffusion mechanism via oxygen vacancies.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...