Characterisation of charge conduction networks in poly(3-hexylthiophene)/polystyrene blends using noise spectroscopy†
Abstract
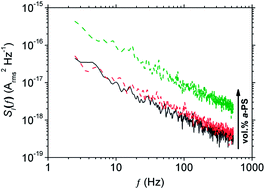
1/f noise spectroscopy is used to investigate charge conduction networks within polymer blend space-charge-limited diodes (SCLDs) fabricated from regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene) (P3HT) and either isotactic-polystyrene (i-PS) or amorphous-polystyrene (a-PS). Conducting AFM measurements showed that i-PS blends have heterogeneous conduction characterised by current ‘hotspots’, whereas a-PS blends showed homogeneous conduction. The difference in conducting networks between blends was clearly revealed when examining the noise spectra for the range of blend devices. Furthermore, the shape of the noise spectra suggested that as the blend composition changed, the charges sampled differing breadths of the density of states. These data suggest that noise measurements can be used as an informative technique to electrically characterise the effects of blend morphology and its effects within polymer electronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...