Gelation properties of self-assembling N-acyl modified cytidine derivatives†
Abstract
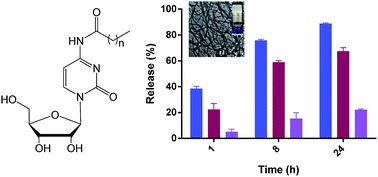
In this study we report the synthesis of new cytidine derived gelators possessing acyl chains of different lengths. These low molecular weight gelators were shown to form self-supporting gels at 0.5% (w/v) in binary systems of aqueous miscible polar organic solvent and water. The representative gels were studied using rheology and their fibrillar structure confirmed by TEM imaging and FTIR. We further demonstrated the use of these gels as potential drug delivery platforms by monitoring release characteristics of both high and low molecular weight fluorescently labelled tracers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...