pH-activatable near-infrared fluorescent probes for detection of lysosomal pH inside living cells†
Abstract
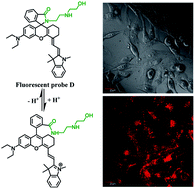
Four near-infrared fluorescent probes (A, B, C and D) have been synthesized, characterized, and evaluated for detection of lysosomal pH inside living cells. The fluorescent probes display highly sensitive and selective fluorescent response to acidic pH as the acidic pH results in drastic structural changes from spirocyclic (non-fluorescent) forms to ring-opening (fluorescent) forms of the fluorescent probes. The fluorescence intensities of the fluorescent probes (B, C and D) increase significantly by more than 200-fold from pH 7.4 to 4.2. The fluorescent probe D bearing the N-(2-hydroxyethyl) ethylene amide residue possesses the advantages of high sensitivity, excellent photostability, good cell membrane permeability, strong pH dependence, and low auto-fluorescence background. It has been successfully applied to selectively stain lysosomes and detect lysosomal pH changes inside normal endothelial and breast cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...