Peptide-based isolation of circulating tumor cells by magnetic nanoparticles†
Abstract
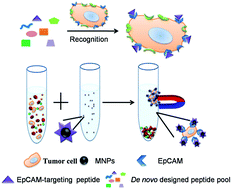
Detection of rare circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in the peripheral blood of metastatic cancer patients has shown promise for improved diagnosis, staging and prognosis of cancers. The epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM) has been revealed to be over-expressed in CTCs while it is absent in normal blood cells and has been used as an efficient diagnosis and therapeutic target on CTCs, especially in CTC isolation and detection. Most of the CTC isolation techniques are based on nanomaterials or nanostructured surfaces functionalized with the EpCAM antibody. Herein, instead of anti-EpCAM, we report a new CTC isolation method with high efficiency by using the EpCAM recognition peptide functionalized iron oxide magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) (Pep@MNPs). The de novo designed peptide, Pep10, with comparable binding affinity KD (1.98 × 10−9 mol L−1) to that of the anti-EpCAM (2.69 × 10−10 mol L−1) is attached onto MNPs via biotin–avidin interaction. We demonstrate that Pep10@MNPs (200 nm) have the comparable capture efficiency (reaching above 90%) and purity (reaching above 93%) to anti-EpCAM@MNPs for breast, prostate and liver cancers from spiked human blood. Furthermore, the captured cells still maintain viability for further molecular biological analysis with this method. The peptide-based CTC isolation method could be beneficial for cancer prognosis and metastasis prevention by increasing the stability and reproducibility.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...