Recyclable antibacterial material: silicon grafted with 3,6-O-sulfated chitosan and specifically bound by lysozyme†
Abstract
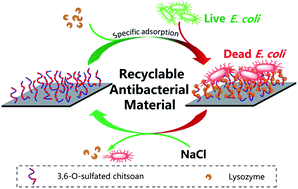
The use of functional material surfaces in antibacterial applications shows great potential. This study proposes a new strategy to evade the decrease in surface antibacterial activity associated with physical adsorption or the covalent modification of antibacterial substances onto material surfaces. 3,6-O-Sulfated chitosan (3,6S-chitosan), as a specific ligand for lysozyme, was synthesized and grafted onto a silicon wafer. The specific adsorption of lysozyme onto a 3,6S-chitosan-modified surface was detected, and the activity of the surface-bound lysozyme was measured. The results showed that the 3,6S-chitosan-modified surface exhibited very high hydrolysis activity for bacterial cell wall components, over 16 times greater than that on the other surfaces. The specific activity of the lysozyme bound on the 3,6S-chitosan-modified surface was approximately 37 000 U mg−1, close to the activity of native lysozyme. The 3,6S-chitosan-modified surface loaded with lysozyme was capable of killing almost all of the E. coli cells attached to the material. Moreover, the surface could be regenerated and its antibacterial activity could be regained through high-salinity treatment. The results suggest that a 3,6S-chitosan-modified surface could be useful for the preparation of new recyclable antibacterial materials through the specific adsorption of lysozyme with 3,6S-chitosan.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...