Dual functions of interface passivation and n-doping using 2,6-dimethoxypyridine for enhanced reproducibility and performance of planar perovskite solar cells†
Abstract
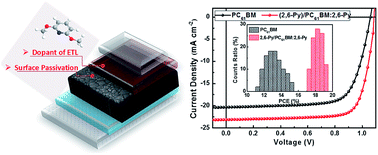
The reproducibility of high-performance perovskite solar cells (PVSCs) remains a major obstacle. Herein, for the first time, we report the use of 2,6-dimethoxypyridine (2,6-Py) for interface chemistry engineering to fabricate reproducible high-efficiency planar perovskite solar cells. The 2,6-Py serves dual functions: (1) as a Lewis base enabling surface passivation of Lewis acid traps (e.g., under-coordinated Pb ions) without corroding the perovskite; (2) as a chemical dopant for [6,6]-phenyl-C61-butyric acid methyl ester (PC61BM) to improve its conductivity and mobility for efficient electron extraction and transport. Thus, through both the surface passivation of the perovskite layer and the doping of the electron transport layer with 2,6-Py, the resultant MAPbI3-based planar solar cells outperform the untreated devices with power conversion efficiency (PCE) significantly improved from 15.53% to 19.41%. The devices with the dual-function treatment yield effectively improved reproducibility with a narrow PCE distribution – that is, around 90% of the devices afford a PCE of over 17.50% (about 90% of the champion PCE), and also display enhanced air stability – that is, they maintain nearly 80% of their initial PCEs after 200 h in ambient air without any encapsulation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...