Monodisperse embedded nanoparticles derived from an atomic metal-dispersed precursor of layered double hydroxide for architectured carbon nanotube formation†
Abstract
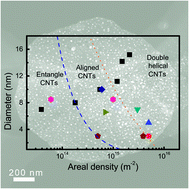
Monodisperse metal nanoparticles (NPs) with high activity and selectivity are among the most important catalytic materials. However, the intrinsic process to obtain well-dispersed metal NPs with tunable high density (ranging from 1013 to 1016 m−2) and thermal stability is not yet well understood. Herein, the preparation of metal NPs with tunable areal density from layered double hydroxide (LDH) precursors in which the metal cations were pre-dispersed at an atomic scale was explored. Large quantities of mesopores induced by the Kirkendall effect were formed on the as-calcined layered double oxide (LDO) flakes. The O atoms bonded with Fe3+ cations were easy to be extracted at a temperature higher than 750 °C, which greatly increased the mobility of Fe. Consequently, coalescence of the reduced Fe atoms into large NPs enhanced the Kirkendall effect, leading to the formation of monodisperse embedded Fe NPs on the porous LDO flakes. The flake morphology of LDHs was well preserved, and the areal density of Fe NPs on the LDO flakes can be well controlled through adjusting the Fe content in the LDH precursor. With higher Fe loading, larger Fe NPs with higher areal density were available. When the areal density was increased from 0.039 to 0.55, and to 2.1 × 1015 m−2, the Fe NPs embedded on the LDO flakes exhibited good catalytic performance for the growth of entangled carbon nanotubes (CNTs), aligned CNTs, and double helical CNTs, respectively. This work provides not only new insights into the chemical evolution of monodisperse NPs from an atomic metal-dispersed precursor, but also a general route to obtain tunable NPs as heterogeneous catalysts for chemical and material production.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...