Probe diffusion in phase-separated bicontinuous biopolymer gels
Abstract
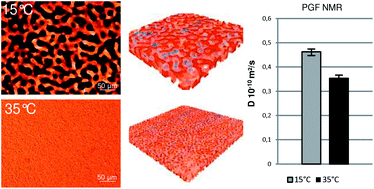
Probe diffusion was determined in phase separated bicontinuous gels prepared by acid-induced gelation of the whey protein isolate–gellan gum system. The topological characterization of the phase-separated gel systems is achieved by confocal microscopy and the diffusion measurements are performed using pulsed field gradient (PFG) NMR and fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching (FRAP). These two techniques gave complementary information about the mass transport at different time- and length scales, PFG NMR provided global diffusion rates in the gel systems, while FRAP enabled the measurements of diffusion in different phases of the phase-separated gels. The results revealed that the phase-separated gel with the largest characteristic wavelength had the fastest diffusion coefficient, while the gel with smaller microstructures had a slower probe diffusion rate. By using the diffusion data obtained by FRAP and the structural data from confocal microscopy, modelling through the lattice-Boltzmann framework was carried out to simulate the global diffusion and verify the validity of the experimental measurements. With this approach it was found that discrepancies between the two experimental techniques can be rationalized in terms of probe distribution between the different phases of the system. The combination of different techniques allowed the determination of diffusion in a phase-separated biopolymer gel and gave a clearer picture of this complex system. We also illustrate the difficulties that can arise if precautions are not taken to understand the system–probe interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...