Nanobubble formation on a warmer substrate†
Abstract
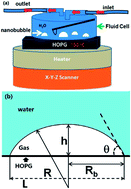
The solvent exchange procedure is an often-used protocol to produce surface nanobubbles. In this procedure, the substrate is exposed to a good solvent for gas which is then mixed and rinsed with a poor solvent for gas and the nanobubbles form on the solid–liquid interface. Here we study the effects of temperatures of the substrate and the first solvent on nanobubble formation. Atomic force microscopy with temperature control was used to examine the formation of nanobubbles at temperatures between 37 °C and 54 °C. It was found that the probability of nanobubble formation was larger on substrates at higher temperatures. Moreover, on warmer substrates we found nanobubbles with lateral extensions up to 8 μm. A morphologic analysis shows that all nanobubbles, including giant nanobubbles, have a similar aspect ratio, independent of the substrate temperature, and that this aspect ratio corresponds to a contact angle between 13° and 22° (on the gas side), much smaller than the macroscopic counterparts. We finally discuss the implications of our results for various theories on nanobubble stability.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...