Luminescent Re(i) and Re(i)/Au(i) complexes as cooperative partners in cell imaging and cancer therapy†
Abstract
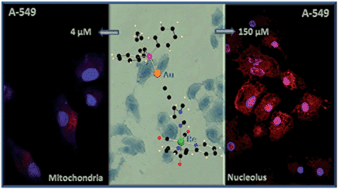
A series of luminescent monometallic fac-[Re(bipy)(CO)3(L)]+ and heterometallic fac-[Re(bipy)(CO)3(L-AuPPh3)]+ complexes, where L is an imidazole, alkynyl-imidazole or alkynyl-pyridine derivative, have been synthesised for the purpose of finding a synergic effect between the excellent photophysical properties of rhenium complexes and the good antiproliferative effects of gold compounds. Cytotoxicity studies performed in human A549 lung cancer cells revealed the importance of the alkynyl–phosphine–gold fragment within the probe to design efficient anticancer agents. Heterometallic Re(I)/Au(I) derivatives presented values of IC50 more than 10 times lower than their analogous Re(I) complexes. In addition, fluorescent cell microscopy pointed out the different biodistribution behaviour of the monometallic and heterometallic families. Whereas the monometallic Re(I) species showed some general cytoplasmatic staining with mitochondrial accumulation, the heterometallic Re(I)/Au(I) derivatives shifted from localising in the mitochondria to the nucleus and nucleolus upon increasing the loading concentration, suggesting a completely different driving force for their localisation pattern. These facts revealed that these bimetallic species can be excellent partners in cell imaging and cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...