Hydrosilylation as an efficient tool for polymer synthesis and modification with methacrylates†
Abstract
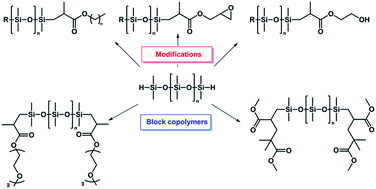
Hydrosilylation is a well-established reaction for the preparation of organo-silicon compounds, in which vinyl groups react with silanes (Si–H) usually catalysed by late transition metal complexes, most often Pt(II) complexes. Hydrosilylation of functional methacrylates provides access to functional poly(dimethylsiloxane)s (PDMS), from appropriate hydride terminated and functional PDMS, in very high yielding reactions without the formation of any side products, odour and without the need for labor-intensive purification. Herein, commercially available telechelic PDMS hydrides (h2PDMS) have been modified with a range of different methacrylates using very low catalytic amounts of commercial Pt(II) catalysts. The products have been characterized by 1H and 13C NMR, SEC, IR and MALDI-ToF MS demonstrating high selectivity and very high reaction yields. The versatility of hydrosilylation has been exploited for the preparation of ABA triblock copolymers using poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate and more structurally demanding vinyl terminated methacrylic macromonomers as obtained by catalytic chain transfer polymerization (CCTP). 1H NMR revealed the formation of solely anti-Markovnikov products and the high tolerance of the reaction towards other functionalities, such as epoxides present in glycidyl methacrylate. The specific Si–H signals in 1H NMR (4.8 ppm) and IR (2126 cm−1) from the Si–H group allow for facile monitoring of the progress of the reaction. SEC and MALDI-ToF MS investigations further highlighted the formation of well-defined polymer systems with near perfectly matching molecular compositions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...