Ligase-assisted, upconversion luminescence resonance energy transfer-based method for specific and sensitive detection of V600E mutation in the BRAF gene
Abstract
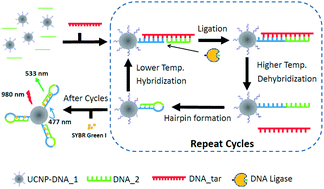
The most common BRAF mutation, V600E, accounts for a variety of cancers. Here we report a highly specific and sensitive method for the detection of the V600E mutation. The detection scheme is based on luminescence resonance energy transfer (LRET) between upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) and an intercalating dye, SYBR Green I. Target DNA serves as the template for two DNA probes, one of them covalently attached to UCNPs, to be ligated into a hairpin-forming DNA strand, which brings SYBR Green I close to the upconversion nanoparticles. The number of the resulting DNA strand is amplified through thermal cycling. The degree of LRET is correlated to the amount of the initial DNA targets. Factors affecting the detection specificity and sensitivity, including ligation temperature, amount of ligase, and number of thermal cycles, have been investigated to optimize the performance of the detection method. The method can easily differentiate the V600E mutation from the wild-type sequence with a mutant-to-wild-type ratio of 1 : 1000. A detection limit of 1 femtomole BRAF V600E mutation is achieved.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...