Original biobased nonisocyanate polyurethanes: solvent- and catalyst-free synthesis, thermal properties and rheological behaviour†
Abstract
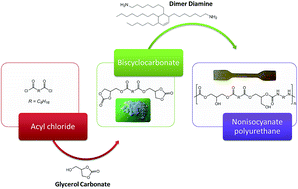
Novel biobased NonIsocyanate PolyUrethanes (NIPUs) were synthesized from dimer-based diamines and sebacic biscyclocarbonate in bulk, and without catalyst. All synthesized NIPUs present biobased contents around 80%. Biscyclocarbonates and final NIPUs were characterized by FTIR and NMR spectroscopy. A specific study was conducted to determine the best carbonate to amine ratio. The influence on the structures and properties of NIPUs with different average amine functionalities, varying from 2.0 to 2.2, was investigated by DSC, SEC and dynamic rheological analyses. Based on FTIR analyses, it was found that the stoichiometric ratio is optimal for the NIPU synthesis to obtain the highest molar masses with appropriate kinetics. However, the results show that the molar masses (up to 22 000 g mol−1) were lower than conventional polyurethanes. A specific structuration due to a higher crosslink degree was observed when the average functionality of the diamine dimer increased. As expected, the glass transition temperature rises in this case. Crosslinked samples were synthesized with an average amine functionality of 2.15 and 2.2. A promising elastomer sample with elongation higher than 600% was then obtained.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...