The effect of growth oxygen pressure on the metal–insulator transition of ultrathin Sm0.6Nd0.4NiO3−δ epitaxial films
Abstract
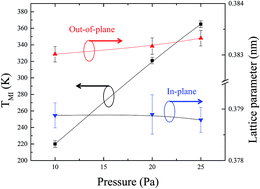
Ultrathin Sm0.6Nd0.4NiO3−δ epitaxial films were deposited by pulsed laser deposition (PLD) onto LaAlO3 (LAO) single crystal substrates. The influence of growth oxygen pressure on the metal–insulator transition (MIT) was investigated. It was found that the MI transition temperature (TMI) of the films decreases remarkably with the decrease of the growth oxygen pressure, while the films' strain state stays almost the same. The increased oxygen vacancies induced by lower growth oxygen pressure, verified by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, seem to be the main cause of such phenomena.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...