Synthesis, biological evaluation and in silico and in vitro mode-of-action analysis of novel dihydropyrimidones targeting PPAR-γ†
Abstract
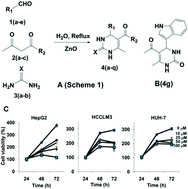
Hepatocellular carcinoma, a fatal liver cancer, affects 600 000 people annually and ranks third in cancer-related lethality. In this work we report the synthesis and related biological activity of novel dihydropyrimidones. Among the tested compounds, 5-acetyl-4-(1H-indol-3-yl)-6-methyl-3,4-dihydropyrimidin-2(1H)-one (4g) was found to be most active towards the HepG2 cell line (IC50 = 17.9 μM), being at the same time 7.6-fold selective over normal (LO2) liver cells (IC50 = 136.9 μM). Subsequently, we identified peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ as a target of compound 4g using an in silico approach, and confirmed this mode-of-action experimentally.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...