Ultrafine carbamazepine nanoparticles with enhanced water solubility and rate of dissolution†
Abstract
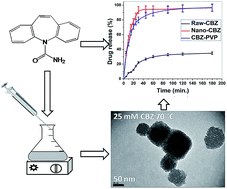
Carbamazepine (CBZ) is an antiepileptic drug having poor water solubility and hence poor bioavailability. Spherical nanoparticles of CBZ with particle size below 50 nm were successfully prepared by the evaporation assisted solvent–antisolvent interaction (EASAI) method. CBZ nanoparticles that are stabilized by polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) were also prepared by the same method. Solubility of CBZ nanoparticles and CBZ–PVP nanoparticles was 11.9 and 21.5 times higher than the raw-CBZ. In vitro dissolution studies showed that almost 100% of the drug was released from CBZ nanoparticles and CBZ–PVP nanoparticles in less than 60 min whereas only 34% of the drug was released from raw-CBZ even after 180 min. The effect of different experimental parameters such as the concentration of drug and the presence of PVP on particle size, morphology, solubility and in vitro drug release rate of CBZ was thoroughly investigated. The spherical morphology of the nanoparticles was confirmed by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and transmission electron microcopy (TEM). FTIR spectroscopy studies revealed that there is hydrogen bonding between PVP and CBZ molecules in the CBZ–PVP nanoparticles. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of CBZ–PVP nanoparticles revealed the subtle change in crystal structure of raw-CBZ. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) studies showed that the nanoparticles were relatively less crystalline than the raw-CBZ.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...