Fluorescent bionanoprobes based on quantum dot-chitosan–O-phospho-l-serine conjugates for labeling human bone marrow stromal cells
Abstract
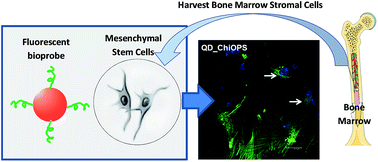
Bone replacement materials might be promising alternatives to autogenous bone transplants during the repair and reconstruction of human bone tissues. However, bone healing is a very complex process, and the roles of phosphatidylserine (PS) and its moieties are not yet completely understood. In the present study, fluorescent quantum dots (QDs) functionalized with chitosan–O-phospho-L-serine (chi–OPS) conjugates have been synthesized and characterized while focusing on their potential applications as nanoprobes for labeling human bone marrow stromal cells (hBMSC). Essentially, chitosan was covalently linked to the peptide (O-phospho-L-serine, OPS) through the formation of amide bonds. In this sequence, these chi–OPS conjugates were utilized as direct capping ligands during CdS QDs (CdS/chi–OPS) biofunctionalization, which was achieved using a single-step process in an aqueous medium at room temperature. The core–shell nanostructures were characterized in detail by UV-visible spectroscopy (UV-Vis), photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) with selected area electron diffraction (SEAD). The TEM images associated with the UV-vis optical absorption results indicated that ultra-small nanocrystals were formed with average diameters ranging from 2.2 to 2.8 nm. In addition, the PL results showed that the nanoconjugates exhibited “green” fluorescent activity under ultraviolet excitation. Cell viability was assessed in vitro via an MTT analysis, revealing that the bioconjugates were not cytotoxic after 3 days of incubation. Moreover, a quantitative flow cytometry (QFC) analysis and confocal fluorescence microscopy (CFA) were performed, verifying the fluorescence-labeling efficiency and the endocytosis of the bionanoprobes by hBMSC. In summary, innovative fluorescent conjugates were developed with properties for use as biomarkers when imaging and detecting bone tissue regeneration and metabolic events.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...