A flexible, nonenzymatic glucose biosensor based on Ni-coordinated, vertically aligned carbon nanotube arrays†
Abstract
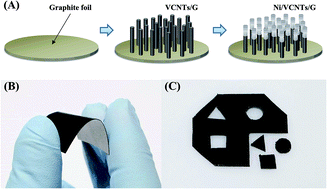
We evaluated the use of flexible biosensors based on Ni-coordinated, vertically aligned carbon nanotubes on a flexible graphite substrate (Ni/VCNTs/G) for the nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose. The Ni/VCNTs/G electrodes were fabricated by a simple process of radiofrequency sputtering and plasma-enhanced chemical vapour deposition. We performed cyclic voltammetry and chronoamperometry for electrochemical characterization of the Ni/VCNTs/G electrodes. In addition, we examined the effect of mechanical bending on their sensing performance. The electrodes exhibited enhanced electrocatalytic activity toward the oxidation of glucose in alkaline solution compared to the bare graphite, Ni particles, and vertically aligned CNTs on graphite. They also exhibited a sensitivity of 950.6 μA mM−1 cm−2 to glucose with a linear range of 0.05 to 1.0 mM and a detection limit of 30 μM. In particular, there was no significant change in the amperometric signal of the electrodes, showing a sensitivity of 910.7 μA mM−1 cm−2 (only a 4% decrease in the initial response) after the 200th bending. Moreover, the Ni/VCNTs/G electrodes were less sensitive to common interfering species such as ascorbic acid, uric acid, galactose, and xylose than to glucose. To summarize, our Ni/VCNTs/G electrodes exhibited enhanced electrocatalytic activity, good sensitivity, a fast response, high selectivity, and excellent mechanical stability. Therefore, we expect that our flexible, nonenzymatic glucose biosensor based on this electrode will open exciting opportunities for wearable, real-time, and/or on-site applications in fields ranging from clinical analysis to industry.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...