Investigation of angiogenesis and its mechanism using zinc oxide nanoparticle-loaded electrospun tissue engineering scaffolds
Abstract
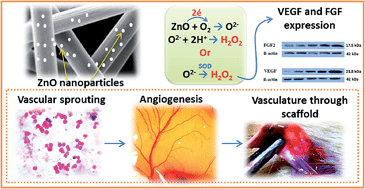
Angiogenesis through tissue engineering scaffolds is an important factor that determines the success of a tissue engineering endeavor. Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles are well known for their ability to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS) which have a potential role in biological systems. ROS can induce angiogenesis through growth factor mediated mechanisms. Here, we report the fabrication of electrospun polycaprolactone scaffolds incorporated with ZnO nanoparticles and their ability to induce angiogenesis. This study demonstrated that the induction of angiogenesis was by the expression of key proangiogenic factors, fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), upregulated due to the presence of ZnO nanoparticles. This is the first report suggesting the use of a metal/metal oxide nanoparticle in tissue engineering scaffolds to enhance angiogenesis.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...