Magneto-structural correlation, antioxidant, DNA interaction and growth inhibition activities of new chloro-bridged phenolate complexes†
Abstract
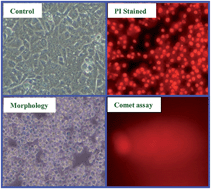
A new class of chloro-bridged dinuclear nickel(II) and copper(II) phenolate complexes (1–8) were synthesized from 4-substituted-2-((2-(piperazin-1-yl)ethylimino)methyl)phenols (L1−4) and characterized. The XRD analysis of complexes 4 and 8 shows two mononuclear units connected through a bridged chlorine atom that gives dinuclear complexes. The stability of the complexes has been determined using a spectrophotometric method. Complexes 5–8 possess significant antioxidant activity against the DPPH radical. The binding studies of complexes with CT-DNA suggest partial intercalative/electrostatic interaction and the cleavage ability for pBR322 DNA shows the involvement of the hydroxyl radical as an intermediate in the cleavage reaction. The IC50 value of complexes 2, 6 and 8 against the HepG2 cell line is comparable with that of cisplatin. To find the extent of nuclear chromatin cleavage, propidium iodide staining and comet assays were employed. Among the newly synthesized complexes, copper(II) complexes exhibited superior biological activity when compared to their nickel(II) analogues.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...