Amino-functionalized ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15, a rapid and efficient adsorbent for the adsorption of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate from green tea extract†
Abstract
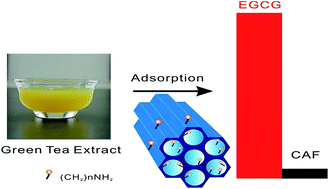
Ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15 with different pore size and organic groups (–SH, –NH2, –COOH) were synthesized. The adsorption of (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) from green tea extract (GTE) was conducted on these functional ordered mesoporous silica SBA-15, which were studied as a class of potential adsorbents. The adsorption performance of EGCG was correlated with the surface chemistry and pore size. Amino-functionalized SBA-15 (SBA-15-NH2) with a large pore size (10.7 nm) exhibited extremely rapid rate as well as high capacity of 287 mg g−1 for adsorbing EGCG at 25 °C, which is much higher than that of other adsorbent previously reported. EGCG rather than CAF were preferred to adsorb onto SBA-15-140 °C-NH2 since the adsorption capacity of EGCG was almost 19 times as high as that of CAF (287 mg g−1 vs. 15 mg g−1). The kinetic data were well fitted with pseudo-second-order kinetics based on an evaluation of the adsorption kinetics. Furthermore, the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms provided additional information for better understanding of the adsorption process. Hydrogen bonding and electrostatic interaction were the main driving forces for the adsorption of EGCG on the SBA-15-NH2s. Considering the excellent adsorption performance, it is expected that mesoporous silica materials are attractive for the separation and enrichment of EGCG.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...